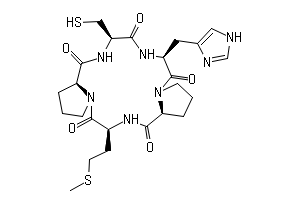
/30CC142AE74BE8BD802585F8007FA3B4/$file/FC108869_structure.png)
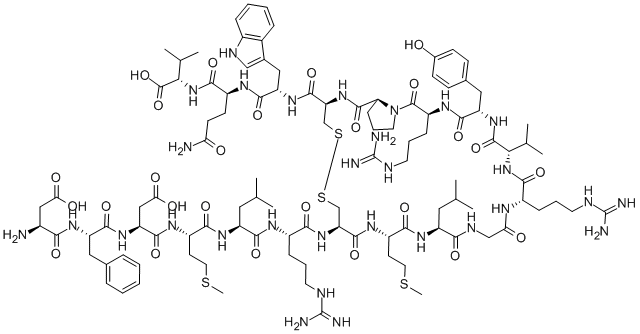
Calcitonin (rat) H-Cys-Gly-Asn-Leu-Ser-Thr-Cys-Met-Leu-Gly-Thr-Tyr-Thr-Gln-Asp-Leu-Asn-Lys-Phe-His-Thr-Phe-Pro-Gln-Thr-Ser-Ile-Gly-V al-Gly-Ala-Pro-NH2 (Disulfide bond)
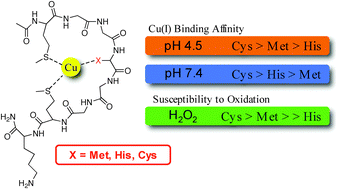
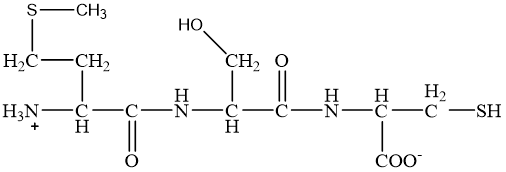
A comparison of methionine, histidine and cysteine in copper(i)-binding peptides reveals differences relevant to copper uptake by organisms in diverse environments - Metallomics (RSC Publishing)

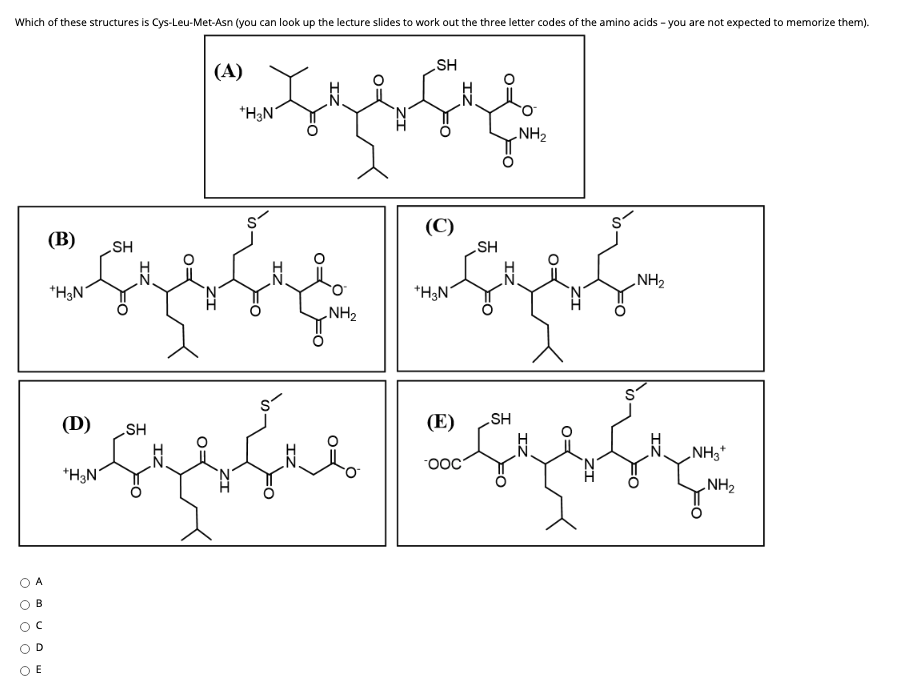
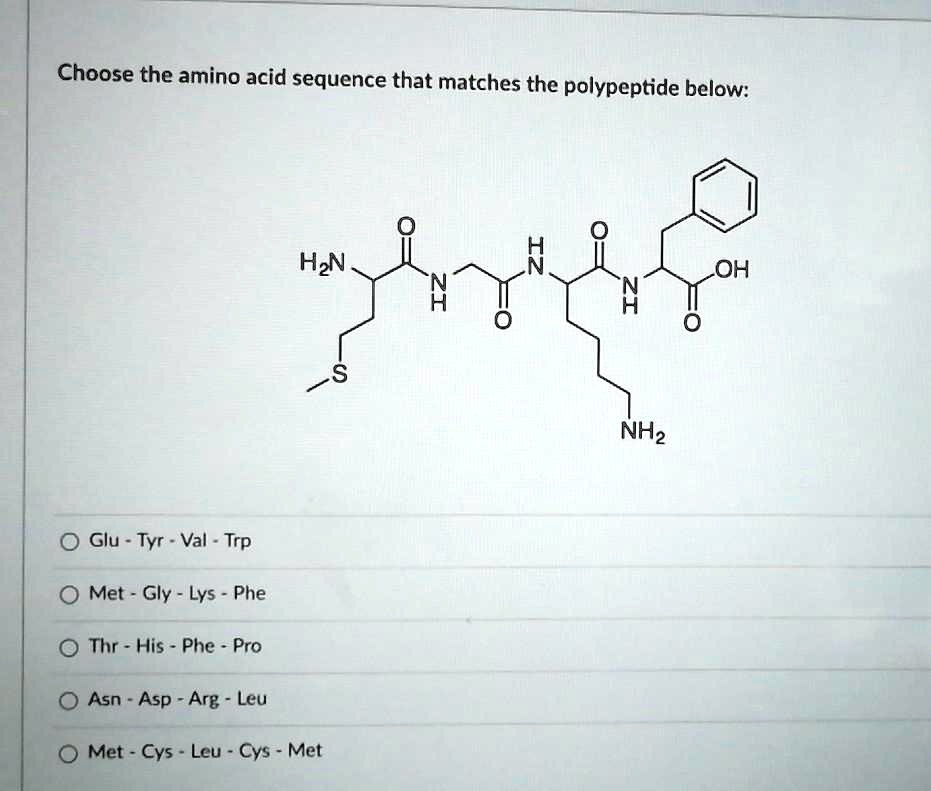
Given the following peptide: Val-Met-Ser-Ile-Phe-Arg-Cys-Tyr-Leu a) Identify the polar amino acids. b) Identify the non-polar amino acids. c) Identify the amino acids that contain sulfur. d) Identify the aromatic amino acids.
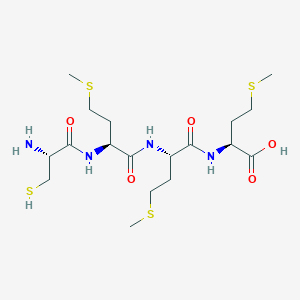

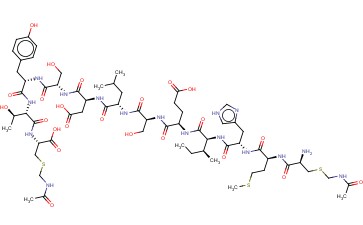
/26C1E09870793EC1802585F8007FA51C/$file/FC109033_structure.png)